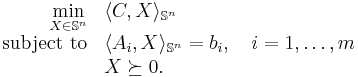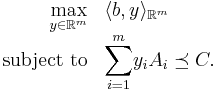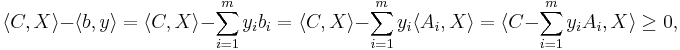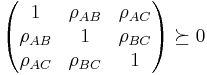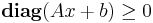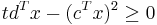Semidefinite programming
Semidefinite programming (SDP) is a subfield of convex optimization concerned with the optimization of a linear objective function over the intersection of the cone of positive semidefinite matrices with an affine space, i.e., a spectrahedron.
Semidefinite programming is a relatively new field of optimization which is of growing interest for several reasons. Many practical problems in operations research and combinatorial optimization can be modeled or approximated as semidefinite programming problems. In automatic control theory, SDP's are used in the context of linear matrix inequalities. SDPs are in fact a special case of cone programming and can be efficiently solved by interior point methods. All linear programs can be expressed as SDPs, and via hierarchies of SDPs the solutions of polynomial optimization problems can be approximated. Finally, semidefinite programming has been used in the optimization of complex systems.
Contents |
Definition
Notation
Denote by 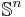 the space of all
the space of all 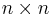 real symmetric matrices. The space is equipped with the inner product (where
real symmetric matrices. The space is equipped with the inner product (where 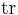 denotes the trace)
denotes the trace) 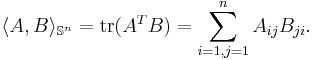
A symmetric matrix is positive semidefinite if all its eigenvalues are nonnegative; we write 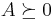 . Similarly,
. Similarly, 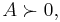
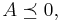 and
and 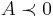 means that
means that  is positive definite, negative semidefinite, and negative definite, respectively. Denote by
is positive definite, negative semidefinite, and negative definite, respectively. Denote by 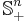 the convex cone of positive semidefinite
the convex cone of positive semidefinite 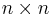 matrices. This cone defines a partial order for
matrices. This cone defines a partial order for 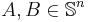 by
by 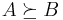 whenever
whenever 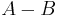 is positive semidefinite,
is positive semidefinite, 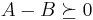 .
.
Primal and dual form
Linear semidefinite programming (SDP) deals with optimization problems of the type
We refer to this problem as a primal semidefinite program (P-SDP). Analogously to linear programming, we introduce a dual semidefinite program (D-SDP)
For convenience, an SDP will often be specified in a slightly different, but equivalent form. For example, linear expressions involving nonnegative scalar variables may be added to the program specification. This remains an SDP because each variable can be incorporated into the matrix  as a diagonal entry (
as a diagonal entry (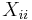 for some
for some 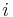 ). To ensure that
). To ensure that 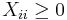 , constraints
, constraints 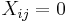 can be added for all
can be added for all 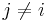 . As another example, note that for any positive semidefinite matrix
. As another example, note that for any positive semidefinite matrix  , there exists a set of vectors
, there exists a set of vectors 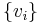 such that the
such that the 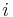 ,
, 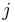 entry of
entry of  is
is 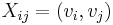 the scalar product of
the scalar product of 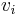 and
and 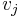 . Therefore, SDPs are often formulated in terms of linear expressions on scalar products of vectors. Given the solution to the SDP in the standard form, the vectors
. Therefore, SDPs are often formulated in terms of linear expressions on scalar products of vectors. Given the solution to the SDP in the standard form, the vectors 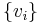 can be recovered in
can be recovered in 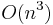 time (e.g., by using an incomplete Cholesky decomposition of X).
time (e.g., by using an incomplete Cholesky decomposition of X).
Duality Theorem
Weak Duality
The weak duality theorem states that the value of the primal SDP is at least the value of the dual SDP. Therefore, any feasible solution to the dual SDP lower-bounds the primal SDP value, and conversely, and feasible solution to the primal SDP upper-bounds the dual SDP value. This is because
where the last inequality is because both matrices are positive semidefinite.
Strong Duality
Under a condition known as Slater's condition, the value of the primal and dual SDPs are equal. This is known as strong duality. Unlike for linear programs, however, not every SDP satisfies strong duality; in general, the value of the dual SDP may lie strictly below the value of the primal.
(i) Suppose the primal problem (P-SDP) is bounded below and strictly feasible (i.e., there exists 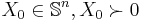 such that
such that 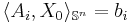 ,
, 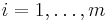 ). Then there is an optimal solution
). Then there is an optimal solution 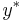 to (D-SDP) and
to (D-SDP) and
(ii) Suppose the dual problem (D-SDP) is bounded above and strictly feasible (i.e., 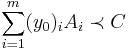 for some
for some 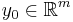 ). Then there is an optimal solution
). Then there is an optimal solution 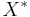 to (P-SDP) and the equality from (i) holds.
to (P-SDP) and the equality from (i) holds.
Examples
Example 1
Consider three random variables  ,
, 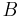 , and
, and 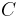 . By definition, their correlation coefficients
. By definition, their correlation coefficients 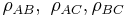 are valid if and only if
are valid if and only if
Suppose that we know from some prior knowledge (empirical results of an experiment, for example) that 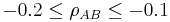 and
and 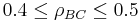 . The problem of determining the smallest and largest values that
. The problem of determining the smallest and largest values that 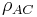 can take is given by:
can take is given by:
- minimize/maximize
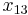
- subject to
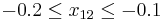
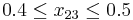
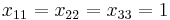
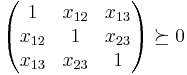
we set 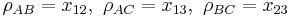 to obtain the answer. This can be formulated by an SDP. We handle the inequality constraints by augmenting the variable matrix and introducing slack variables, for example
to obtain the answer. This can be formulated by an SDP. We handle the inequality constraints by augmenting the variable matrix and introducing slack variables, for example
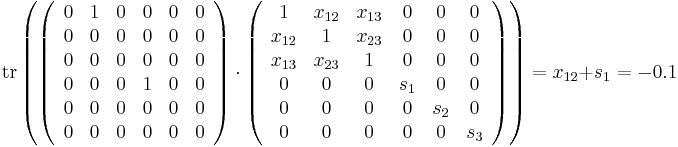
Solving this SDP gives the minimum and maximum values of 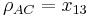 as
as 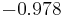 and
and 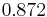 respectively.
respectively.
Example 2
Consider the problem
- minimize
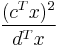
- subject to
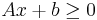
where we assume that 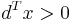 whenever
whenever 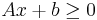 .
.
Introducing an auxiliary variable 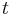 the problem can be reformulated:
the problem can be reformulated:
- minimize
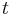
- subject to
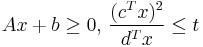
In this formulation, the objective is a linear function of the variables 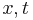 .
.
The first restriction can be written as
where the matrix 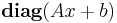 is the square matrix with values in the diagonal equal to the elements of the vector
is the square matrix with values in the diagonal equal to the elements of the vector 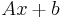 .
.
The second restriction can be written as
or equivalently
- det
![\underbrace{\left[\begin{array}{cc}t&c^Tx\\c^Tx&d^Tx\end{array}\right]}_{D}\geq 0](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/4716c3a1c00adcf62801a21e76330fdb.png)
Thus 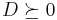 .
.
The semidefinite program associated with this problem is
- minimize
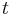
- subject to
![\left[\begin{array}{ccc}\textbf{diag}(Ax%2Bb)&0&0\\0&t&c^Tx\\0&c^Tx&d^Tx\end{array}\right] \succeq 0](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/ca74059d280420b89954ac97cf1af814.png)
Example 3 (Goemans-Williamson MAX CUT approximation algorithm)
Semidefinite programs are important tools for developing approximation algorithms for NP-hard maximization problems. The first approximation algorithm based on an SDP is due to Goemans and Williamson (JACM, 1995). They studied the MAX CUT problem: Given a graph G = (V, E), output a partition of the vertices V so as to maximize the number of edges crossing from one side to the other. This problem can be expressed as an integer quadratic program:
- Maximize
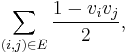 such that each
such that each 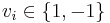 .
.
Unless P = NP, we cannot solve this maximization problem efficiently. However, Goemans and Williamson observed a general three-step procedure for attacking this sort of problem:
- Relax the integer quadratic program into an SDP.
- Solve the SDP (to within an arbitrarily small additive error
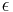 ).
). - Round the SDP solution to obtain an approximate solution to the original integer quadratic program.
For MAX CUT, the most natural relaxation is
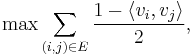 such that
such that 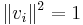 , where the maximization is over vectors
, where the maximization is over vectors 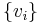 instead of integer scalars.
instead of integer scalars.
This is an SDP because the objective function and constraints are all linear functions of vector inner products. Solving the SDP gives a set of unit vectors in 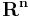 ; since the vectors are not required to be collinear, the value of this relaxed program can only be higher than the value of the original quadratic integer program. Finally, a rounding procedure is needed to obtain a partition. Goemans and Williamson simply choose a uniformly random hyperplane through the origin and divide the vertices according to which side of the hyperplane the corresponding vectors lie. Straightforward analysis shows that this procedure achieves an expected approximation ratio (performance guarantee) of 0.87856 - ε. (The expected value of the cut is the sum over edges of the probability that the edge is cut, which is simply arccos of the angle between the vectors at the endpoints of the edge over
; since the vectors are not required to be collinear, the value of this relaxed program can only be higher than the value of the original quadratic integer program. Finally, a rounding procedure is needed to obtain a partition. Goemans and Williamson simply choose a uniformly random hyperplane through the origin and divide the vertices according to which side of the hyperplane the corresponding vectors lie. Straightforward analysis shows that this procedure achieves an expected approximation ratio (performance guarantee) of 0.87856 - ε. (The expected value of the cut is the sum over edges of the probability that the edge is cut, which is simply arccos of the angle between the vectors at the endpoints of the edge over 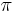 . Comparing this probability to
. Comparing this probability to 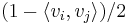 , in expectation the ratio is always at least 0.87856.) Assuming the Unique Games Conjecture, it can be shown that this approximation ratio is essentially optimal.
, in expectation the ratio is always at least 0.87856.) Assuming the Unique Games Conjecture, it can be shown that this approximation ratio is essentially optimal.
Since the original paper of Goemans and Williamson, SDPs have been applied to develop numerous approximation algorithms. Recently, Prasad Raghavendra has developed a general framework for constraint satisfaction problems based on the Unique Games Conjecture.[1]
It has also been shown that the MAX CUT approximation is a kind of Locality Sensitive Hash and is related to the Simhash algorithm.
Algorithms
There are several types of algorithms for solving SDPs. These algorithms output the value of the SDP up to an additive error 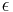 in time that is polynomial in the program description size and
in time that is polynomial in the program description size and 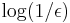 .
.
Interior point methods
Most codes are based on interior point methods (CSDP, SeDuMi, SDPT3, DSDP, SDPA). Robust and efficient for general linear SDP problems. Restricted by the fact that the algorithms are second-order methods and need to store and factorize a large (and often dense) matrix.
Bundle method
The code SBmethod formulates the SDP problem as a nonsmooth optimization problem and solves it by the Spectral Bundle method of nonsmooth optimization. This approach is very efficient for a special class of linear SDP problems.
Other
Algorithms based on augmented Lagrangian method (PENSDP) are similar in behavior to the interior point methods and can be specialized to some very large scale problems. Other algorithms use low-rank information and reformulation of the SDP as a nonlinear programming problem (SPDLR).
Software
The following codes are available for SDP:
SDPA, CSDP, SDPT3, SeDuMi, DSDP, PENSDP, SDPLR, SBmeth
SeDuMi runs on MATLAB and uses the Self-Dual method for solving general convex optimization problems.
Applications
Semidefinite programming has been applied to find approximate solutions to combinatorial optimization problems, such as the solution of the max cut problem with an approximation ratio of 0.87856. SDPs are also used in geometry to determine tensegrity graphs, and arise in control theory as LMIs.
References
- ^ Raghavendra, P. 2008. Optimal algorithms and inapproximability results for every CSP?. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual ACM Symposium on theory of Computing (Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, May 17–20, 2008). STOC '08. ACM, New York, NY, 245-254.
- Lieven Vandenberghe, Stephen Boyd, "Semidefinite Programming", SIAM Review 38, March 1996, pp. 49–95. pdf
- Monique Laurent, Franz Rendl, "Semidefinite Programming and Integer Programming", Report PNA-R0210, CWI, Amsterdam, April 2002. optimization-online
- E. de Klerk, "Aspects of Semidefinite Programming: Interior Point Algorithms and Selected Applications", Kluwer Academic Publishers, March 2002, ISBN 1-4020-0547-4.
- Robert M. Freund, "Introduction to Semidefinite Programming (SDP), SDP-Introduction
External links
- Links to introductions and events in the field
- Lecture notes from Laszlo Lovasz on Semidefinite Programming
- Software
- Overview of existing software
- NEOS Solvers: A server that runs multiple algorithms for solving SDPs and other optimization problems
- SeDuMi: (Self-Dual-Minimization) solves optimization problems over symmetric cones (this includes semidefinite optimization).
- YALMIP: MATLAB optimization toolbox and frontend for many sdp solver
- cvx: a MATLAB frontend that uses either SeDuMi or SDPT3
- cvxopt: a python solver
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||